[Click the names for pronunciation]
Email: s1feng [at] ucsd.edu
I am a Ph.D. student in the Neurosciences Graduate Program at University of California San Diego (UCSD), advised by Virginia R. de Sa. I previously received my B.S. in Cognitive Science with a specialization in Machine Learning and Neural Computation also from UCSD.
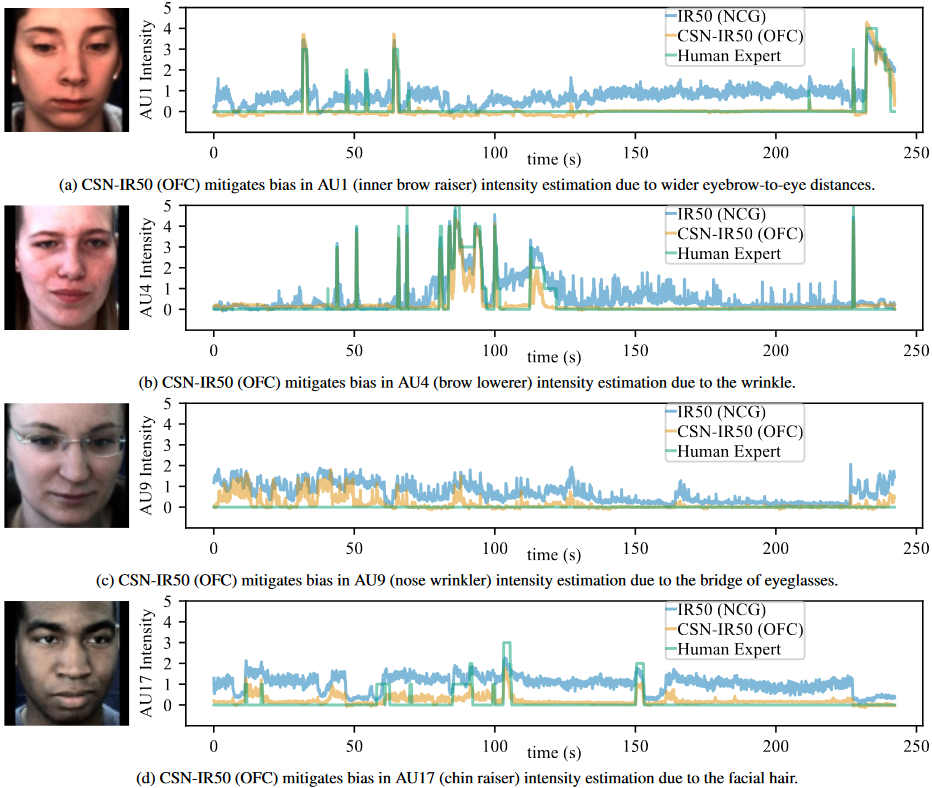
My research interests lie in computer vision, cognitive modeling, and computational neuroscience. My current research focuses on facial expression recognition and its applications. Active projects include: (1) improvement of automated facial expression recognition systems; (2) incorporation of facial expression recognition into large language models (LLMs); (3) application of facial expression recognition in education; (4) application of facial expression recognition in assisting the improvement of image generation algorithms.